How To Find Multiplicity Of A Molecule
The molecular charge and the spin multiplicity are essential input for a molecular calculation. Spin multiplicity -n 1 -2 1 -1 ignore paired electrons and -1 1 0 respectively.

Pin On Nucleophilic Substitution Reactions
The program requires an input of multiplicity 2total spin 1.
How to find multiplicity of a molecule. Calculate many energies of the molecule each time assuming a different spin multiplicity until you have considered all of the possible candidates and pick the one that has the lowest energy. The multiplicity is often equal to the number of possible orientations of the total spin relative to the total orbital angular momentum L and therefore to the number of neardegenerate levels that differ only in their spinorbit interaction energy. The zero associated with this factor x 2 x 2 has multiplicity 2 because the factor x2 x 2 occurs twice.
In general normal organic molecules will have charges of zero and spin multiplicities of one. I have an undergraduate-level understanding of chemistry up to the point where I understand orbital filling 1s2s2p for a given element and its ion of varying charge state. Mutliplicity usually only works with hydrogens on neighbouring carbons.
Assuming the interactionbetween the two solids is suciently weak the multiplicity of the combined system is justthe product of the individual multiplicities for the two solids. The n plus one rule allows us to predict how many Peaks we would expect to see for a signal in an NMR spectrum so if we think about the signal for one proton if that proton has n neighboring protons we would expect to see n plus one Peaks on the NMR spectrum the n plus one rule only applies when the neighboring protons are chemically equivalent to each other so in the last video. The peak at 1 ppm is the methyl group with an integral of 3H.
Multiplicity is defined as the energy level at 2S1 where S is the total spin angular momentum. Nitrogen z7 1s 2 2s 2 2p 3 1 1 1 S3times frac 1 2. The number of times a given factor appears in the factored form of the equation of a polynomial is called the multiplicity.
This is the multiplicity of a system if we can actually distinguish between each of the objects. Turn off atom manipulation Off. Species having unpaired electrons in both mixed alignment In this case spin multiplicity n -n 1 where n number of unpaired electrons in each alignment.
Diagram of molecular oxygen can also be used to explain the reactivity of molecular oxygen. But in the case of a test tube full of molecules we cannot distinguish each molecule instead we can only observe if a molecule is in state A or state B heads or tails. The x- intercept x 1 x 1 is the repeated solution of factor x13 0 x.
Alternatively look at the spectrum the other way around. In the case of charged species radicals or open-shell molecules these keywords are necessary to specify the correct state of the system. When the multiplicity is 1 2 3 4 5 they are termed as singlets doublets triplets quartets and quintets respectively.
Gaussian09 determines if a requested chargemultiplicity is correct via electron count atoms specified charge and the standard equation for multiplicity 2S1 where S spin angular momentum. The more general formula for this is 2nI 1 where I is the magnetic spin number of the given nucleus. Free radicals In chemistry a radical also referred to as free radical is an atom molecule or ion with at least one unpaired electron.
Do spectroscopy experiments and find the ground state most stable version of the molecule that way. If there is an oxygen on one side of the methylene all three neighbouring hydrogens must be on a carbon on the other side. There is a formula for predicating the number of peaks base on the neighboring hydrogens and that is known as the n 1 rule where n is the number of neighboring protons.
Of the macrostate of the combinedsystem determined byqqAqBfor a givenqAandqB. The superscript three read as triplet indicates that the. For example the ground state of the carbon atom is a 3 P state.
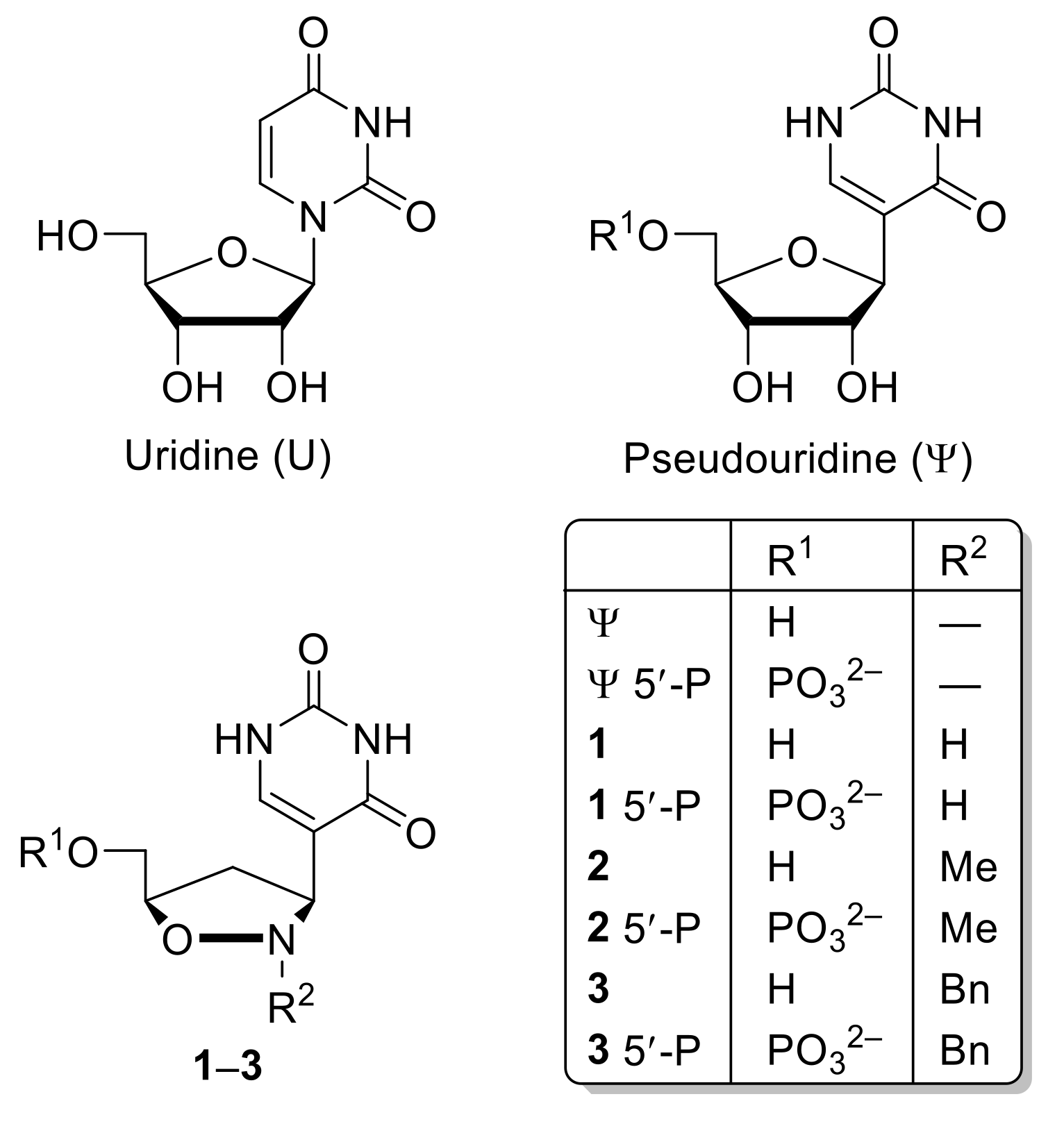
Molecules Free Full Text A Pseudouridine Isoxazolidinyl Nucleoside Analogue Structural Analysis A Morphological Approach Html

Hf Is Polar Or Nonpolar Covalent Bond Covalent Bonding Polar Bond

Pin On Nmr Spectroscopy Practice Problems

Molecular Orbital Theory Bonding Anti Bonding Mo Chemical Bonding Molecular Theories Chemistry

Pin On Orgo Cheat Sheets Tutorials And Reference Material

The Nitrobenzene Molecule Download Scientific Diagram

Unpaired Electron Number Of Different Molecules With Calculation By Download Table

Pin On Nmr Spectroscopy Practice Problems

A Fragment Of A Single Dna Molecule B Scaled Schematic Download Scientific Diagram

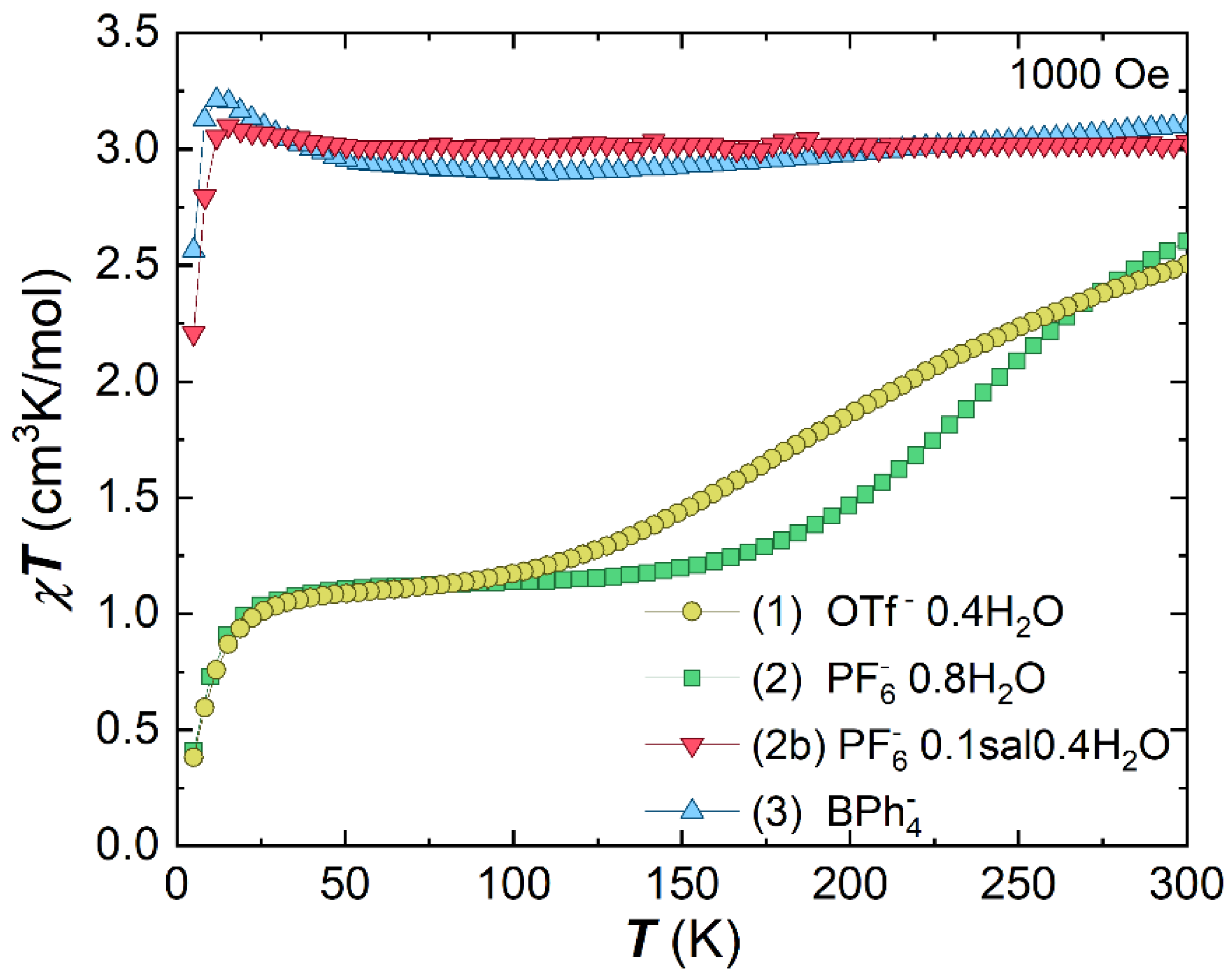
Molecules Free Full Text Modulation Of Mn3 Spin State By Guest Molecule Inclusion Html
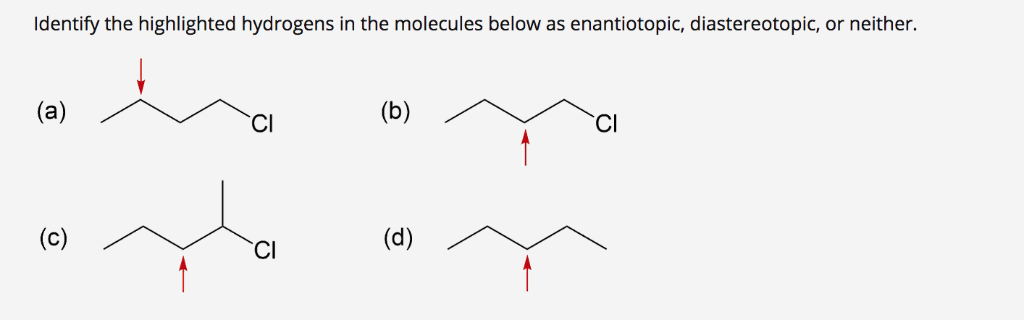
Solved Identify The Highlighted Hydrogens In The Molecule Chegg Com

H2 Covalent Bond Chart Potential Energy Covalent Bonding Chemistry

Molecular Orbital Theory Types Methods Rules Examples And Videos

Turning Ortho Para Directors Into Meta Directors And Vice Versa Organic Chemistry Organic Chem Chemistry

Carbohydrates Summary Sheet Study Guide Teaching Chemistry Chemistry Organic Chemistry

What Makes A Good Leaving Group In Nucleophilic Substitution And Elimination Reactions Chemistry Help Chemistry Teaching Chemistry

Nucleophilic Substitution Reactions An Introduction Organic Chemistry Reactions Reactions Chemistry


Posting Komentar untuk "How To Find Multiplicity Of A Molecule"